ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
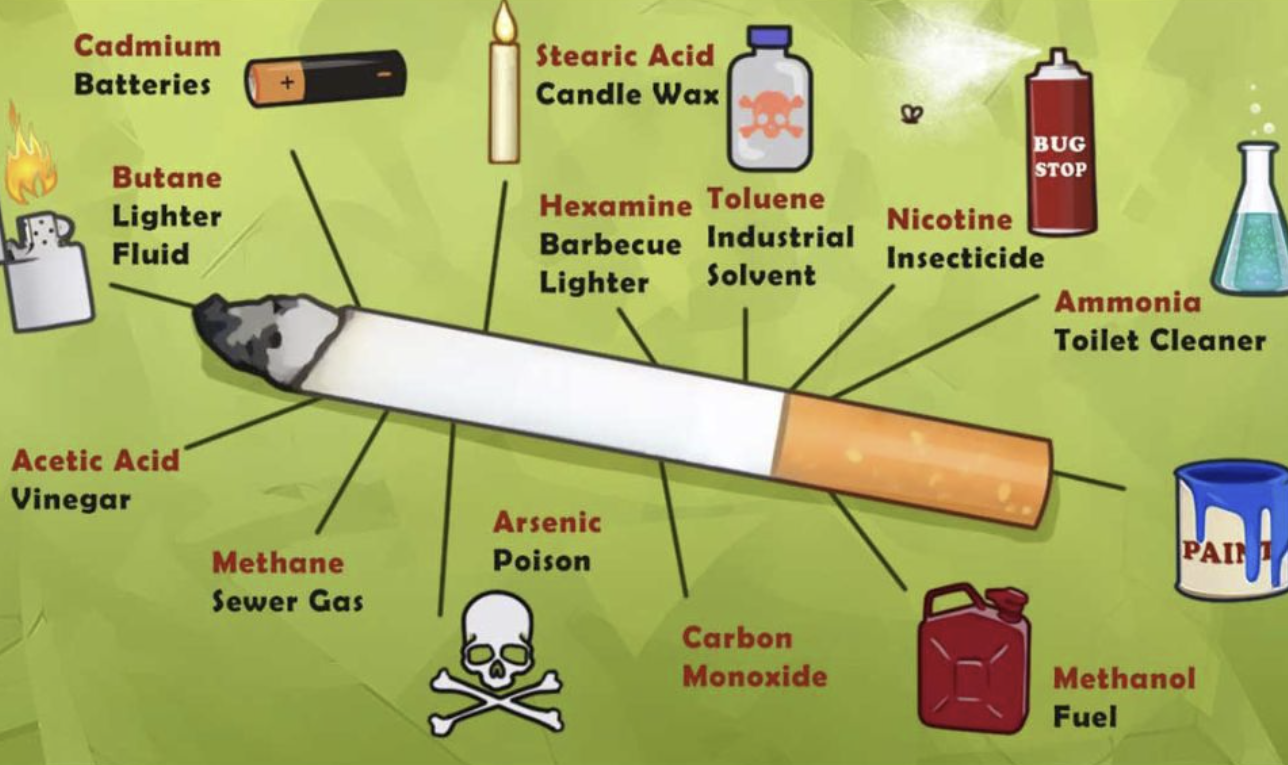
Ever time you smoke, this is what you are actually consuming
Acetic acid, known for giving vinegar its characteristic smell and taste, is also present in cigarette smoke. Inhalation of acetic acid can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat, and prolonged exposure may cause respiratory problems.
Toluene: Industrial Solvent
Toluene is used as an industrial solvent in paint thinners, nail polish removers, and adhesives. Inhaling toluene can cause dizziness, headaches, and neurological damage, adding another layer of harm from cigarette smoke.
Nicotine: The Addictive Agent
Nicotine is the primary addictive substance in cigarettes. It stimulates the release of dopamine, creating a sense of pleasure and reward. However, nicotine addiction leads to increased tolerance and dependence, making it difficult to quit. Nicotine also raises blood pressure and heart rate, contributing to cardiovascular diseases.
Carbonate: Various Forms
Carbonates, such as calcium carbonate, are used in various industries, including construction and manufacturing. In cigarette smoke, carbonates contribute to respiratory irritation and can exacerbate pre-existing lung conditions.
The Combined Effect
The combination of these chemicals makes cigarette smoke a lethal cocktail. Each substance contributes to a range of health issues, from respiratory problems and cardiovascular disease to various forms of cancer and systemic toxicity. Chronic inhalation of these chemicals significantly increases the risk of developing severe health conditions and reduces overall life expectancy.
The Takeaway
Understanding the full spectrum of harmful substances in cigarettes underscores the gravity of smoking’s impact on health. Cigarettes are not just a source of nicotine and tar; they are a delivery system for a wide range of industrial and household chemicals. This knowledge can serve as a powerful deterrent against smoking and a compelling reason for smokers to seek help in quitting.
